CS144-4

CS144-4
幻雪CS144-4
前言cmake - - build build - - target check3如下就可以开始lab4了
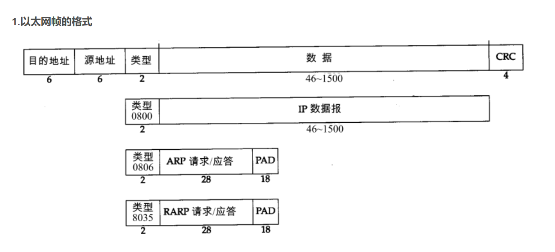
做着这部分最好的就是了解一下报文的类型,和结构关系。我当时做的时候在里面绕了很多弯,比如说误以为ARP以太网包是带普通数据报的,当时想是ARP顺便发过去,后面发现不是,ARP以太网包只含ARP,普通数据以太网包只含普通数据报文(IPV4)。
实验开始
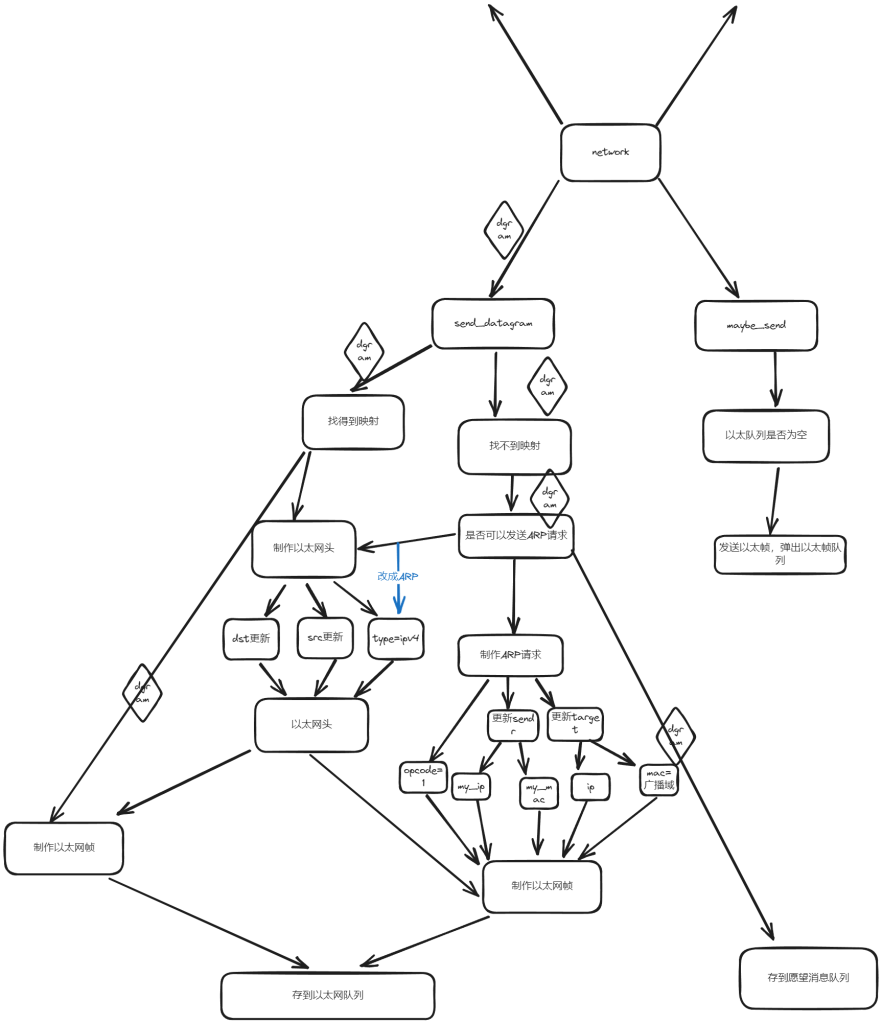
鉴于之前我思路不清晰导致一个lab就在调试方面浪费太多太多时间,我后面使用一些图的关系来表示当时的思路
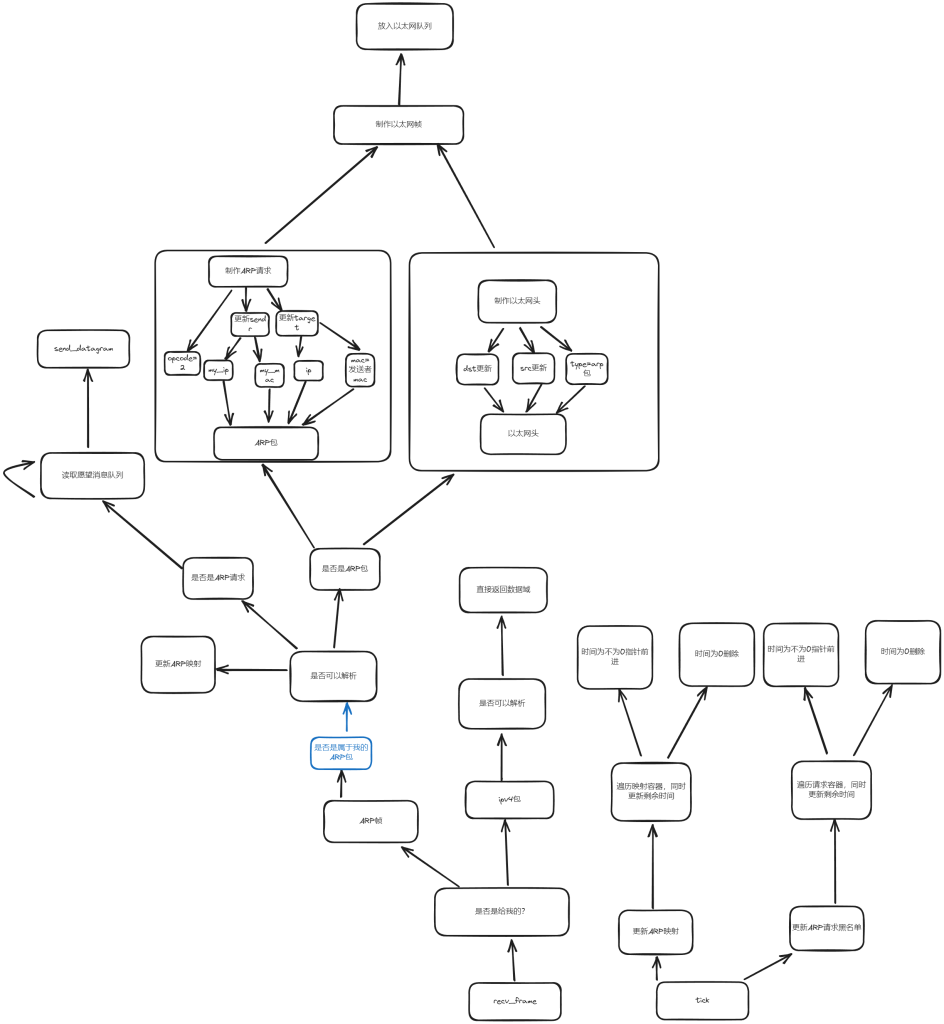
包有两种那么他们的一个关系是如何的?
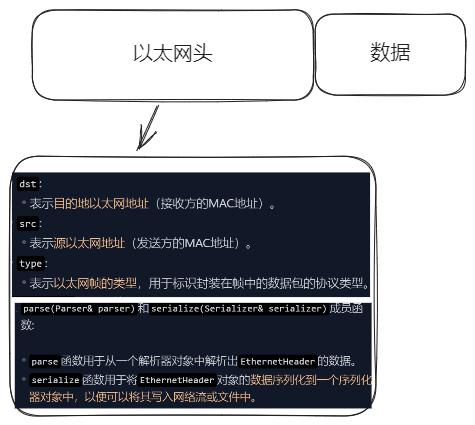
ARP 包和 ipv 4 包,最大的不同其实也就是以太网包的东西不同,以太网有一个以太网头部和以太网主体部分,以太网头部存储的只有 mac 地址(发送和接收,Ip 的部分分析是由主体部分进行一个拆包实现的,对其包涵的东西进行一个拆包,但是主体仍然存在 mac 地址,这个 mac 地址才是真正需要去注意的,他们只是套着以太网帧的头套干着不同的事情
为什么以太网头和ip头都要有mac地址?
传递数据就像是间谍换马甲一样,进入一个国家就穿上一个马甲,也就是 mac 地址只有关于这两个交互国家的,而其中的真正目的 mac 是在主体部分,最后传递到对方手上的时候,以太网帧帧只是从对方的网关的 mac 到对方设备的 mac,mac 地址仅对于当前的局域网或链路是有意义的,并且它们在数据包通过网络传输的过程中会一直变化,直到到达最终的目标设备。而跨越多个网络(国家)的长途传输过程中涉及到的比如 IP 地址等信息则藏于以太网帧的负载(Payload)之内。好处显而易见的实现了一个隐藏 mac 和 ip 的功能保证安全性,同时只关注下一跳实现起来也简单。
代码
在实验过程中要注意实现recv_frame( const EthernetFrame& frame )的时候就算是可以接受的信息也不代表ARP就一定是要你发,也就是说确认是否属于可接收的信息,和检测是否需要你发送是并不包含的,例外就是ARP你可能作为中间进行传递,但并不是一定让你发送你的ARP。而检查是否是你的ARP需要mac地址和ip的双重检测
以下是我实现的代码,需要自己思考的小伙伴就可以停下了
network_interface.cc1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
using namespace std;
// ethernet_address: Ethernet (what ARP calls "hardware") address of the interface
// ip_address: IP (what ARP calls "protocol") address of the interface
// ethernet_address: 以太网(ARP协议中称为“硬件”)接口的地址
// ip_address: IP(ARP协议中称为“协议”)接口的地址
NetworkInterface::NetworkInterface( const EthernetAddress& ethernet_address, const Address& ip_address )
: ethernet_address_( ethernet_address ), ip_address_( ip_address )
{
cerr << "DEBUG: Network interface has Ethernet address " << to_string( ethernet_address_ ) << " and IP address "
<< ip_address.ip() << "\n";
}
// dgram: the IPv4 datagram to be sent
// next_hop: the IP address of the interface to send it to (typically a router or default gateway, but
// may also be another host if directly connected to the same network as the destination)
// dgram: 要发送的IPv4数据报
// next_hop: 要将数据报发送到的接口的IP地址(通常是路由器或默认网关,但如果与目的地在同一网络上直接连接,
// 也可能是另一台主机)
// Note: the Address type can be converted to a uint32_t (raw 32-bit IP address) by using the
// Address::ipv4_numeric() method.
// 注意:Address类型可以通过使用Address::ipv4_numeric()方法转换为uint32_t(原始的32位IP地址)。
void NetworkInterface::send_datagram( const InternetDatagram& dgram, const Address& next_hop )
{
EthernetHeader ethernet_header_;
EthernetFrame ethernet_Frame_;
//目的地已知
auto mac_address= arp_map_.find(next_hop.ipv4_numeric());
if(mac_address!=arp_map_.end()){
// cout<<"目的地已知"<<endl;
ethernet_header_.dst=mac_address->second.macAddress;
ethernet_header_.src=ethernet_address_;
ethernet_header_.type=ethernet_header_.TYPE_IPv4;
ethernet_Frame_.header=ethernet_header_;
ethernet_Frame_.payload=serialize(dgram);
}
//目的地未知,发送ARP帧来取得对应的ip地址与mac映射
else {
// cout<<"目的地未知"<<endl;
//判断是否需要发送(是否找得到记录)
if(ethernet_frame_ARPMessage_map_.find(next_hop.ipv4_numeric())!=
ethernet_frame_ARPMessage_map_.end()){
// cout<<"ARP请求缓冲中"<<endl;
return;
}
// cout<<"执行ARP请求"<<endl;
ARPMessage new_arp_msg;
//设置状态码为请求
new_arp_msg.opcode=ARPMessage::OPCODE_REQUEST;
new_arp_msg.sender_ethernet_address=ethernet_address_;
new_arp_msg.sender_ip_address=ip_address_.ipv4_numeric();
//将发送地址设置成广播地址,但是此处出现了地址错误,说明广播地址是只在以太网帧当中的
new_arp_msg.target_ip_address=next_hop.ipv4_numeric();
//添加以太网头部信息
ethernet_header_.dst=ETHERNET_BROADCAST;
ethernet_header_.src=ethernet_address_;
ethernet_header_.type=ethernet_header_.TYPE_ARP;
//封装以太网帧
ethernet_Frame_.header=ethernet_header_;
ethernet_Frame_.payload= std::move( serialize( new_arp_msg ) );
//放入arp网络优化表,起始行时间是5000ms
ethernet_frame_ARPMessage_map_[next_hop.ipv4_numeric()]=5000;
//那么这次是数据也要保存的,因为有可能不知道mac地址,但是仍然存在想要发送消息的愿望
InternetDatagram_buffer[next_hop.ipv4_numeric()].push_back(dgram);
}
//存入到以太网的处理队列之中
ethernet_frame_buffer_deque.push_back(ethernet_Frame_);
(void)dgram;
(void)next_hop;
}
// frame: the incoming Ethernet frame
// frame: 进来的以太网帧
optional<InternetDatagram> NetworkInterface::recv_frame( const EthernetFrame& frame ){
//判断如果mac不是广播或者本地的就直接返回(不是给你的信息)
if(frame.header.dst!=ethernet_address_&&frame.header.dst!=ETHERNET_BROADCAST){
return nullopt;
}
// cout<<"----------------NetworkInterface::recv_frame-----------------"<<endl;
//传入的是IPV4包
InternetDatagram internet_datagram;
if(frame.header.type==EthernetHeader::TYPE_IPv4){
// cout<<"----------------EthernetHeader::TYPE_IPv4-----------------"<<endl;
if(parse(internet_datagram,frame.payload)){
return internet_datagram;
}
return nullopt;
}
//传入的是ARP帧
else if(frame.header.type==EthernetHeader::TYPE_ARP){
ARPMessage arp_msg;
bool is_effective_arp=parse(arp_msg,frame.payload);
//需要去判断一下是不是要你发的arp包,即使是发给你的包也有可能是广播的形式,所以也就是要做到mac和ip的双重验证
if ( arp_msg.target_ip_address != ip_address_.ipv4_numeric() ){
return nullopt;
}
if(is_effective_arp){
//设置缓存
DeviceInfo device_info{arp_msg.sender_ethernet_address,30000};
//如果有值直接覆盖,如果没有创建(更新)
arp_map_[arp_msg.sender_ip_address]={device_info};
//应该回复什么?
//如果是对方发的是ARP包,我们需要把之前未说的种种发送给对方
if(arp_msg.opcode==ARPMessage::OPCODE_REPLY){
//把之前没说过的话,都倾述出来
//转换一下地址
cout<<"正在发送未处理的数据包的循环前arp_msg.opcode:"<<arp_msg.opcode<<endl;
Address send_ip_address=Address::from_ipv4_numeric(arp_msg.sender_ip_address);
for(auto &it : InternetDatagram_buffer[arp_msg.sender_ip_address]){
send_datagram(it,send_ip_address);
cout<<"正在发送未处理的数据包的循环中,arp_msg.opcode:"<<arp_msg.opcode<<endl;
}
InternetDatagram_buffer[arp_msg.sender_ip_address].clear();
}
//如果对方发的是请求,要我们回复arp包
else{
//建立arp包
ARPMessage new_arp_msg;
//建立包装
EthernetHeader ethernet_header_;
EthernetFrame ethernet_Frame_;
//设置状态码为响应
new_arp_msg.opcode=ARPMessage::OPCODE_REPLY;
new_arp_msg.sender_ethernet_address=ethernet_address_;
new_arp_msg.sender_ip_address=ip_address_.ipv4_numeric();//这里只是处理了ipv4说明有可能出现ipv6需要过滤
//交换源发送端mac和ip
new_arp_msg.target_ethernet_address=arp_msg.sender_ethernet_address;
new_arp_msg.target_ip_address=arp_msg.sender_ip_address;
ethernet_Frame_.payload=serialize(new_arp_msg);
//设置类型
ethernet_header_.type=ethernet_header_.TYPE_ARP;
//目标地址和源地址交换
ethernet_header_.dst=frame.header.src;
ethernet_header_.src=ethernet_address_;
//替换以太网头
ethernet_Frame_.header=ethernet_header_;
//放入准备队列
ethernet_frame_buffer_deque.push_back(ethernet_Frame_);
}
}
return nullopt;
}
(void)frame;
return nullopt;
}
// ms_since_last_tick: the number of milliseconds since the last call to this method
// ms_since_last_tick: 自上次调用此方法以来的毫秒数
void NetworkInterface::tick( const size_t ms_since_last_tick )
{
//更新映射,遍历一遍全部更新就是了
for (auto it = arp_map_.begin(); it != arp_map_.end(); ) {
it->second.existenceTime=it->second.existenceTime>ms_since_last_tick?
it->second.existenceTime-ms_since_last_tick:
0;
if (it->second.existenceTime==0) {
it = arp_map_.erase(it);
} else {
++it;
}
}
//更新ARP请求时间
for (auto it =ethernet_frame_ARPMessage_map_.begin(); it != ethernet_frame_ARPMessage_map_.end(); ) {
it->second=it->second>ms_since_last_tick?
it->second-ms_since_last_tick:
0;
if (it->second==0) {
it = ethernet_frame_ARPMessage_map_.erase(it);
} else {
++it;
}
}
(void)ms_since_last_tick;
}
optional<EthernetFrame> NetworkInterface::maybe_send()
{
/**
* 按照我们实现的相应部分,这一部分的应该只返回一个消息即可
*/
//没准备好就发空的
if(ethernet_frame_buffer_deque.empty()){
return nullopt;
}
//准备好了就发过去
EthernetFrame frame=ethernet_frame_buffer_deque.front();
ethernet_frame_buffer_deque.pop_front();
return frame;
}
network_interface.hh1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
// 定义一个结构体来存储MAC地址和存在时间
struct DeviceInfo {
EthernetAddress macAddress;
uint64_t existenceTime; // 存在时间,ms为单位
};
struct send_ARPMessages
{
uint32_t ip_ipv4;
uint64_t existenceTime;
};
// A "network interface" that connects IP (the internet layer, or network layer)
// with Ethernet (the network access layer, or link layer).
// This module is the lowest layer of a TCP/IP stack
// (connecting IP with the lower-layer network protocol,
// e.g. Ethernet). But the same module is also used repeatedly
// as part of a router: a router generally has many network
// interfaces, and the router's job is to route Internet datagrams
// between the different interfaces.
// The network interface translates datagrams (coming from the
// "customer," e.g. a TCP/IP stack or router) into Ethernet
// frames. To fill in the Ethernet destination address, it looks up
// the Ethernet address of the next IP hop of each datagram, making
// requests with the [Address Resolution Protocol](\ref rfc::rfc826).
// In the opposite direction, the network interface accepts Ethernet
// frames, checks if they are intended for it, and if so, processes
// the the payload depending on its type. If it's an IPv4 datagram,
// the network interface passes it up the stack. If it's an ARP
// request or reply, the network interface processes the frame
// and learns or replies as necessary.
// “网络接口”连接IP(互联网层或网络层)
// 与以太网(网络接入层或链路层)。
// 这个模块是TCP/IP协议栈的最底层
// (将IP与下层网络协议,例如以太网连接起来)。但是,相同的模块也会在路由器中重复使用:
// 一个路由器通常有多个网络接口,路由器的工作是在不同接口之间路由互联网数据报。
// 网络接口将数据报(来自“客户”,例如TCP/IP协议栈或路由器)转换为以太网帧。
// 为了填写以太网目的地址,它会查找每个数据报的下一个IP跳转的以太网地址,
// 使用[地址解析协议](\ref rfc::rfc826)进行请求。
// 在相反的方向上,网络接口接受以太网帧,检查它们是否是为它所设计的,如果是的话,
// 根据其类型处理负载。如果是IPv4数据报,
// 网络接口会将其向上传递。如果是ARP请求或回复,
// 网络接口会处理帧并学习或必要时回复。
// 定义一个结构体来存储MAC地址和存在时间
class NetworkInterface
{
private:
// Ethernet (known as hardware, network-access, or link-layer) address of the interface
// 以太网(又称硬件、网络接入层或链路层)接口的地址mac地址
EthernetAddress ethernet_address_;
// IP (known as Internet-layer or network-layer) address of the interface
// IP(又称互联网层或网络层)接口的地址
Address ip_address_;
// uint64_t NI_cur_time_;//当前的接口时间
// uint64_t NI_pre_time_;//之前的接口时间
uint64_t max_arp_map_existenceTime_=30000;//30秒的最大时间映射
std::unordered_map<uint32_t, DeviceInfo> arp_map_{}; // ARP映射表,键为IP地址字符串
std::unordered_map<uint32_t,uint64_t> ethernet_frame_ARPMessage_map_{};//缓解网络堵塞,减少arp风暴
std::deque<EthernetFrame> ethernet_frame_buffer_deque{};//以太网队列
std::unordered_map<uint32_t,std::list<InternetDatagram>> InternetDatagram_buffer{};//缓存期待发送的消息
public:
// Construct a network interface with given Ethernet (network-access-layer) and IP (internet-layer)
// addresses
// 使用给定的以太网(网络接入层)和IP(互联网层)地址构造一个网络接口
NetworkInterface( const EthernetAddress& ethernet_address, const Address& ip_address );
// Access queue of Ethernet frames awaiting transmission
// 访问等待传输的以太网帧队列
std::optional<EthernetFrame> maybe_send();
// Sends an IPv4 datagram, encapsulated in an Ethernet frame (if it knows the Ethernet destination
// address). Will need to use [ARP](\ref rfc::rfc826) to look up the Ethernet destination address
// for the next hop.
// ("Sending" is accomplished by making sure maybe_send() will release the frame when next called,
// but please consider the frame sent as soon as it is generated.)
// 发送一个IPv4数据报,封装在一个以太网帧中(如果它知道以太网目的地址)。
// 将需要使用[ARP](\ref rfc::rfc826)来查找下一个跳转的以太网目的地址。
// (“发送”是通过确保maybe_send()在下次调用时会释放帧来完成的,
// 但请考虑一旦帧生成就认为它已经发送。)
void send_datagram( const InternetDatagram& dgram, const Address& next_hop );
// Receives an Ethernet frame and responds appropriately.
// If type is IPv4, returns the datagram.
// If type is ARP request, learn a mapping from the "sender" fields, and send an ARP reply.
// If type is ARP reply, learn a mapping from the "sender" fields.
// 接收一个以太网帧并作出适当响应。
// 如果类型是IPv4,返回数据报。
// 如果类型是ARP请求,从“发送者”字段学习映射,并发送一个ARP回复。
// 如果类型是ARP回复,从“发送者”字段学习映射。
std::optional<InternetDatagram> recv_frame( const EthernetFrame& frame );
// Called periodically when time elapses
// 定期调用,当时间流逝时
void tick( size_t ms_since_last_tick );
};